Operators -
There are various types of operators in C language including all the basic functions.
These are used to manipulate data and variables.
C operators can be classified into following types:
- Arithmetic operators
- Relational operators
- Logical operators
- Bitwise operators
- Assignment operators
- Conditional operators
- Special operators
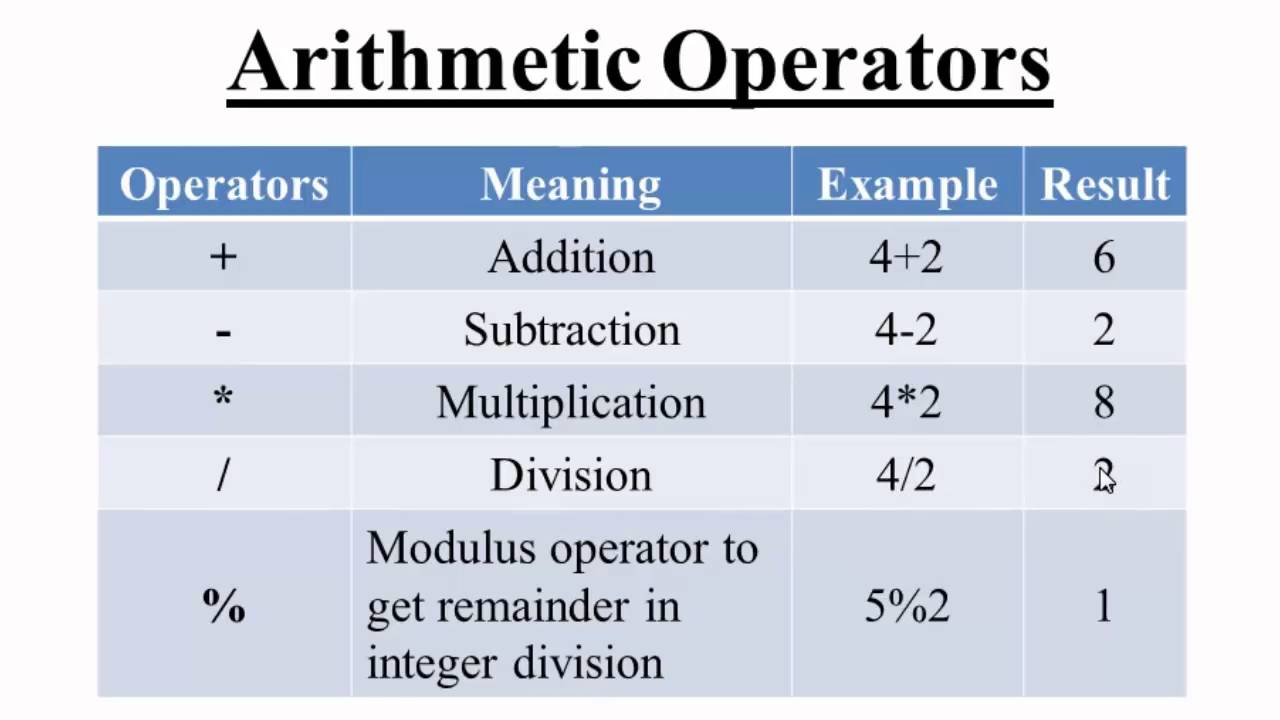
Arithmetic operators -
C supports all arithmetic operators.
Relational operators -
These are used to compare various variables and inputs. These are used for checking equality or which is greater or lesser etc.
Let a=10 , b=0;
This is a substitute of if else statement using basic operators( ? : ).
It is also known as Ternary Operators.
The syntax of a conditional operator is :
Logical operators -
These are 3 in number.
- && - Logical And [Both must satisfy the condition]
- || - Logical Or [Any one or both must satisfy]
- ! - Logical Not [changes the result]
Whenever the input value is 0 ; it will print 0(false); and for the rest prints 1(true)
Let us take an example -Let a=10 , b=0;
- a&&b = 0 (false) [As b=0]
- a||b=1 (true) [As a=1]
- !a=0 (false) [As a is 1[true]; not will change its value to 0(false)]
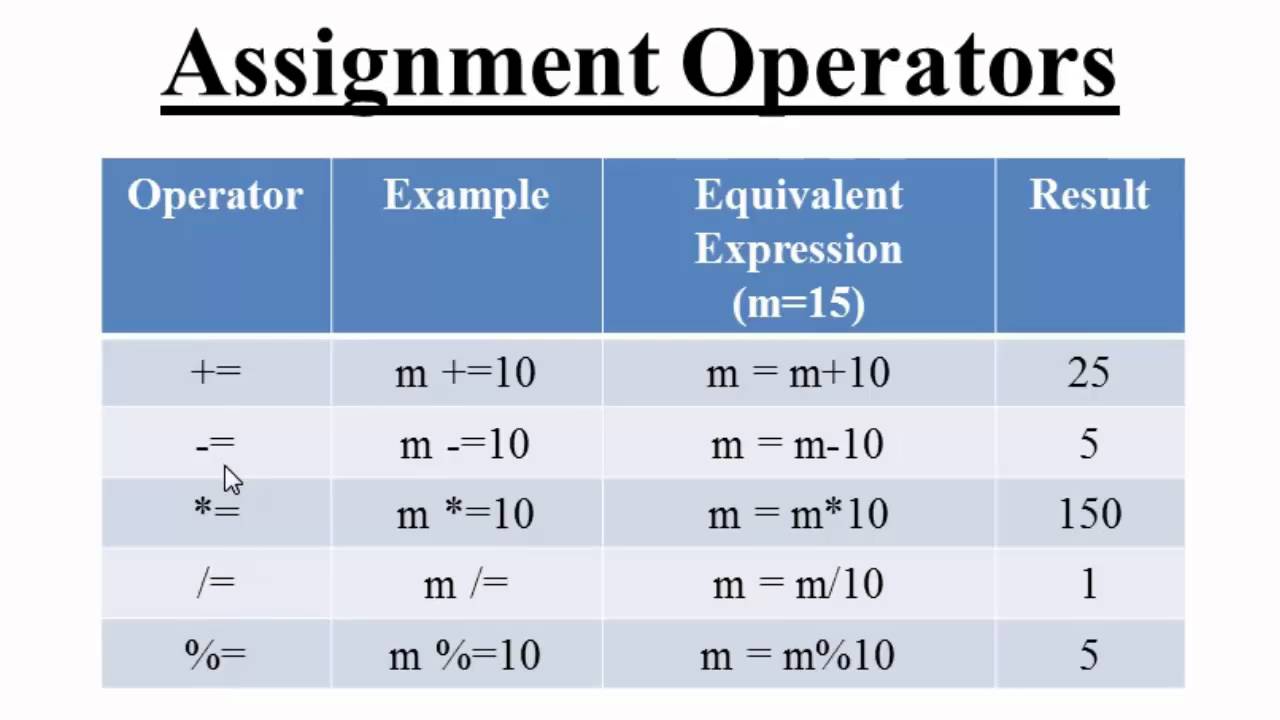
Assignment operators -
These are used to assign values. And follows as shown below -

Conditional operators -
This is a substitute of if else statement using basic operators( ? : ).It is also known as Ternary Operators.
The syntax of a conditional operator is :
expression 1 ? expression 2: expression 3
Explanation:
- The question mark "?" in the syntax represents the if part.
- The first expression (expression 1) generally returns either true or false, based on which it is decided whether (expression 2) will be executed or (expression 3)
- If (expression 1) returns true then the expression on the left side of " : " i.e (expression 2) is executed.
- If (expression 1) returns false then the expression on the right side of " : " i.e (expression 3) is executed.
Special Operators -
- & - defines the address to the input.
- sizeof - Tells the size of the value inserted.
- * - Adds a pointer to the variable.
Bitwise Operators -
These are the operators that act on the bits. These do not work on float or double data types.
- Bitwise And
- Bitwise Or
- Bitwise Xor
- Left shift
- Right shift
Now lets see truth table for bitwise
&, | and ^| a | b | a & b | a | b | a ^ b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
The bitwise shift operator, shifts the bit value. The left operand specifies the value to be shifted and right one tells the no of spaces.





0 Comments