# Data Types -
In the C programming language, data types are declarations for memory locations or variables that determine the characteristics of the data that may be stored and the methods (operations) of processing that are permitted involving them.
C language supports 2 different type of data types:
C language supports 2 different type of data types:
- Primary data types:These are fundamental data types in C namely integer(
int), floating point(float), character(char) andvoid. - Derived data types:Derived data types are nothing but primary datatypes but a little twisted or grouped together like array, stucture, union and pointer.
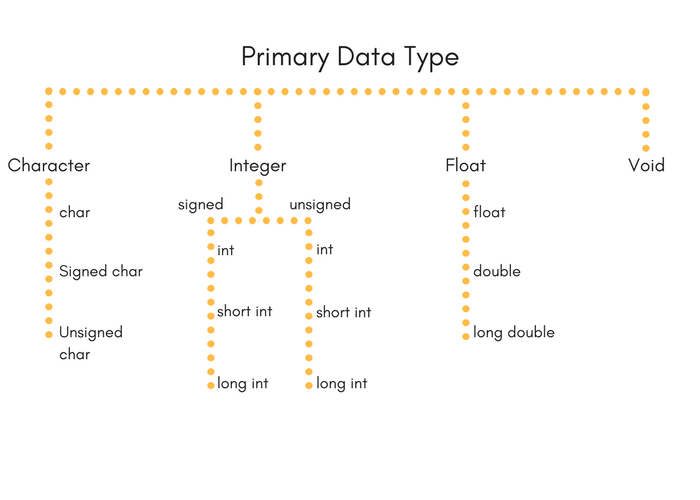
Integer type
Integers are used to store whole numbers
.
Size and range of Integer type on 16-bit machine:
| Type | Size(bytes) | Range |
|---|---|---|
| int or signed int | 2 | -32,768 to 32767 |
| unsigned int | 2 | 0 to 65535 |
| short int or signed short int | 1 | -128 to 127 |
| unsigned short int | 1 | 0 to 255 |
| long int or signed long int | 4 | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
| unsigned long int | 4 | 0 to 4,294,967,295 |
Floating point type
Floating types are used to store real numbers.
Size and range of Integer type on 16-bit machine
| Type | Size(bytes) | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Float | 4 | 3.4E-38 to 3.4E+38 |
| double | 8 | 1.7E-308 to 1.7E+308 |
| long double | 10 | 3.4E-4932 to 1.1E+4932 |
Character type
Character types are used to store characters value.
Size and range of Integer type on 16-bit machine
| Type | Size(bytes) | Range |
|---|---|---|
| char or signed char | 1 | -128 to 127 |
| unsigned char | 1 | 0 to 255 |
void type
void type means no value. This is basically used for the functions that return no values.




0 Comments